Screening insecticides for efficacy or tolerance
Maarten Jongsma and colleagues use EntoLab to detect changes in insect behavior that provide a sensitive method for identifying and quantifying resistance development. They tested this approach with pyrethrins against aphids.
Posted by
Published on
Sun 20 Sep. 2020
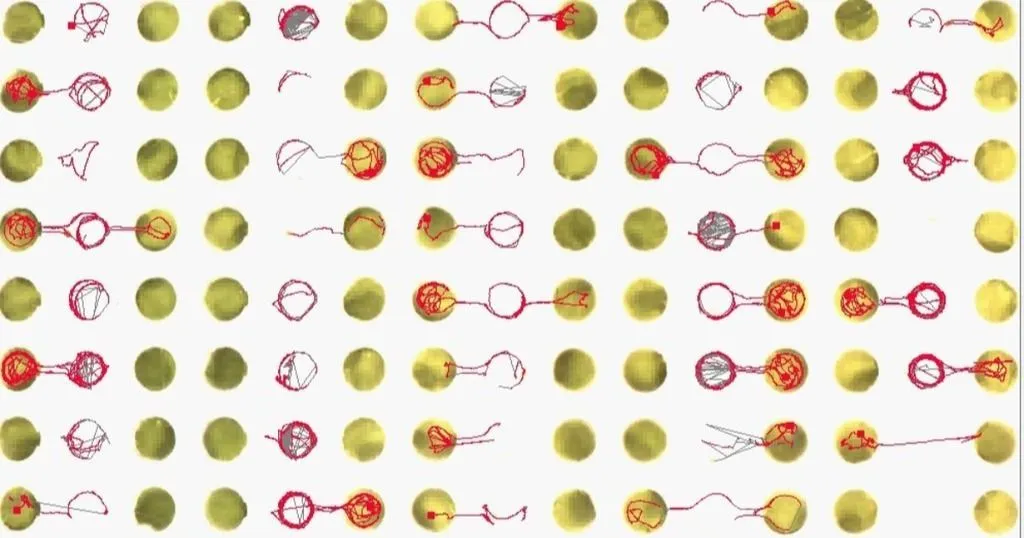
Screening repellence of pyrethrin pesticide formulations
Pesticides against aphids are often primarily focused on behavior modification rather than on causing mortality post-ingestion of host plant material in order to prevent virus transmission. To prevent persistent virus transmission, it is usually essential that the insects don’t probe for a sustained period of time and reach the phloem. That process usually takes about 3 minutes so any formulation that can reduce this residence time to less than 3 minutes potentially works well to prevent transmission. Pyrethrins have the property that once applied to a leaf surface they don’t kill but tend to repel the landed insect. Yet formulations are further improved to enhance this feature by adding co-factors. This was tested at Wageningen Plant Research, where researchers could show that, relative to a control formulation, pausing events (~probe duration) on test leaves lasted indeed less than 3 minutes. The experiments were conducted using EntoLab, the novel automated system for high-throughput screening of insect behavior.
Pesticide resistance
Monitoring of pesticide resistance is an important activity to prevent losing these control measures in food production. The methods for doing this are scarce but one efficient way would be to characterize insects individually or at the population level relative to the pesticide or transgenic crop. EntoLab could detect any modification in behavior or survival and provide a novel sensitive method for identifying and quantifying resistance development. It could also be used to identify the genetic basis and mechanism underlying the resistance or tolerance trait.
Automated screening of aphid choice behavior
The movie below shows video tracking of aphids in EntoLab (1 hour recording played at 16x normal speed).
The assay plate contains 40 T-maze arenas, showing tracks of aphids given a choice between a control and test treatment to evaluate the repellency of the formulation. Each arena consists of a neutral zone (center, white) and two zones with a leaf cutting (green).
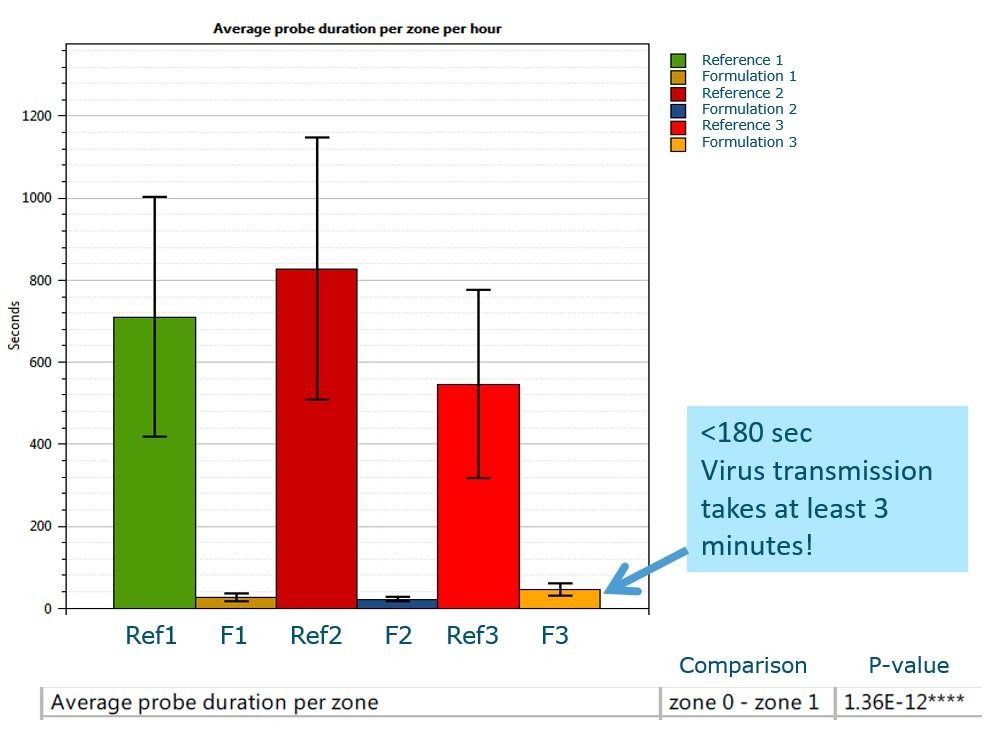
Graphical and statistical summary of the analysis results.
Testing viruses as biocontrol agents
A fundamental question in virology is how insect baculoviruses modify the behavior of the caterpillar host to promote virus spread and transmission. For this purpose, infected and non-infected L2 larvae of Spodoptera exigua were simply placed inside the transparent arena plates and tracked for several hours to measure the distance travelled. The answers of such research may ultimately aid in the selection of the most appropriate virus variants for biocontrol of lepidopteran pest insects.

Related Posts

6 TED talks to kick off your academic year

Non-invasive home cage testing of epilepsy in mice
