Fear, anxiety, and stress
Many psychiatric illnesses are depression- or anxiety-related
disorders. Behavioral tests with rodents are crucial to get insights on the underlying
mechanisms and eventually find new treatments.
Rodents and zebrafish are potentially great models to study fear, anxiety, and stress-related disorders. Common behavioral tasks are:
- Elevated plus maze or zero maze
- Open field
- Novel tank diving test

Fear and anxiety in rodents

Rodents prefer dark and enclosed areas, as it is perceived a safer
environment against predators. This innate aversion to light is used in test set-ups to investigate
anxiety and fear-related behaviors such as staying in the dark, freezing, and hyperactivity.
The open field, elevated plus maze, zero maze, and light-dark box are well-validated tests
that offering a safer, darker environment and an open (often well-lit) area. More anxious animals
tend to hug the walls in an open field, a behavior known as thigmotaxis, or spend more time in the
closed-off arms in an elevated plus maze. Bolder animals start exploring the open areas sooner and
spend more time there.
Stay ahead in behavioral research!
Subscribe to Noldus Newsline
- Discover innovations – Be the first to know about new tools and software to advance your research and get insights that help you stay ahead.
- See real research in action – Get inspired by real-world studies from our community, discovering fresh approaches for your work.
- Access exclusive perks – Receive early updates on promotions, product releases, and events crafted for you.
Methods for studing fear, anxiety, and stress in rodents
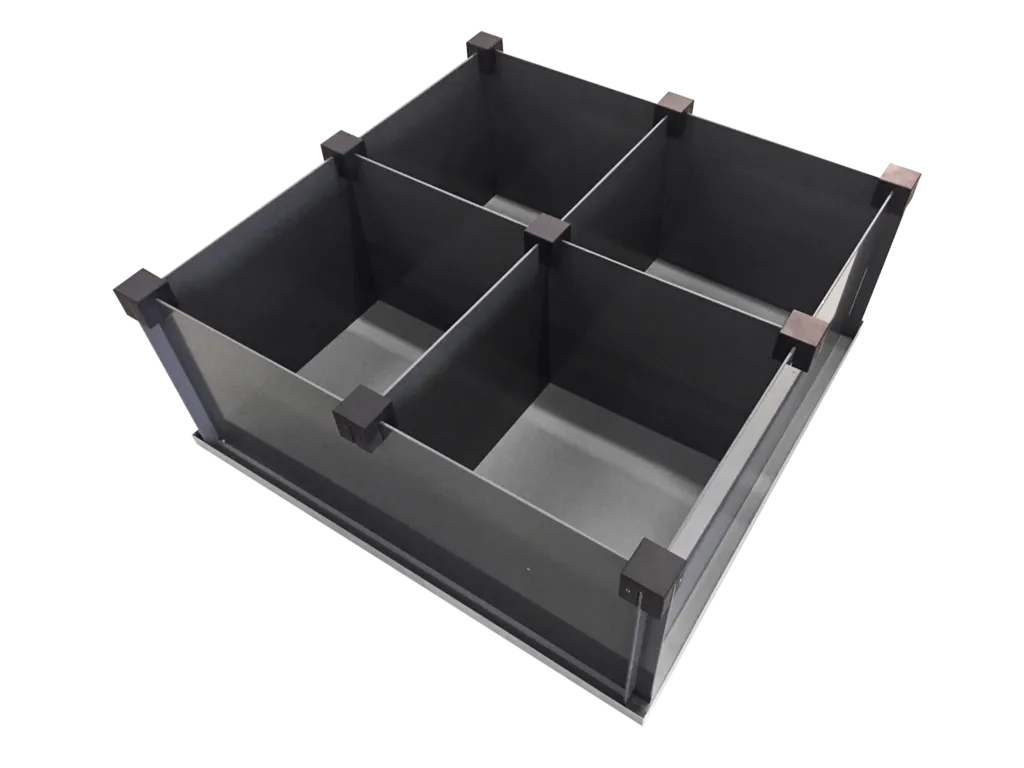

Open field
The open field test is a straight-forward test to investigate activity, anxiety-related and exploratory behavior of rodents.
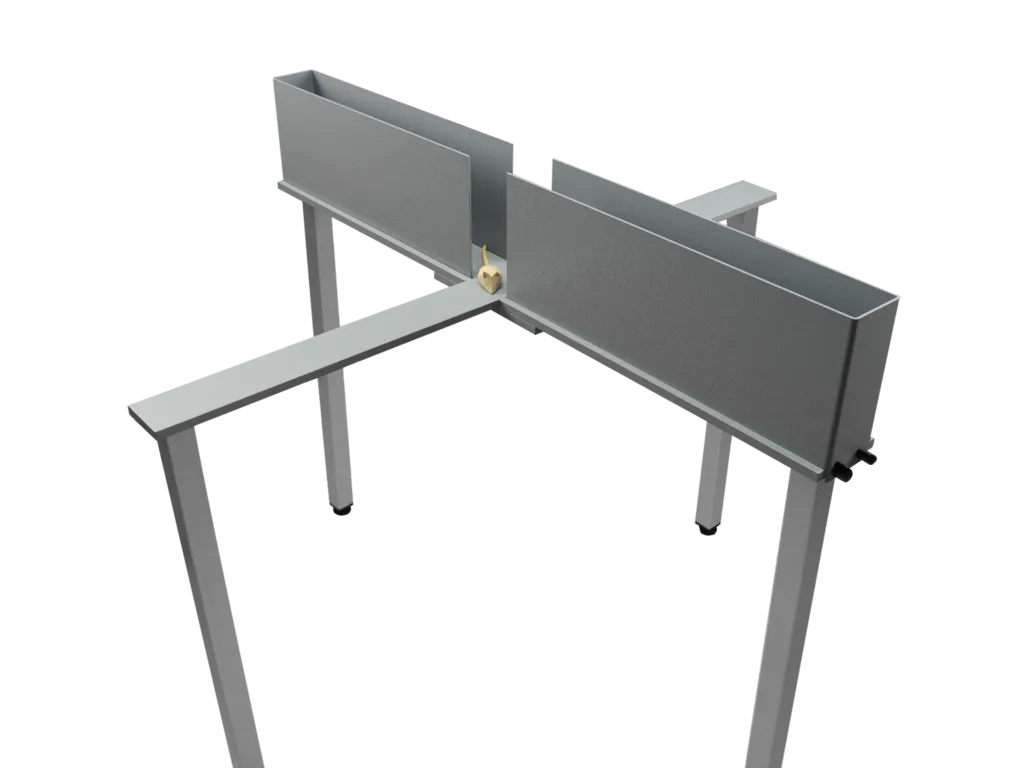

Elevated plus maze
The elevated plus maze is a well-characterized behavioral paradigm, one of the most used tests for anxiety research.
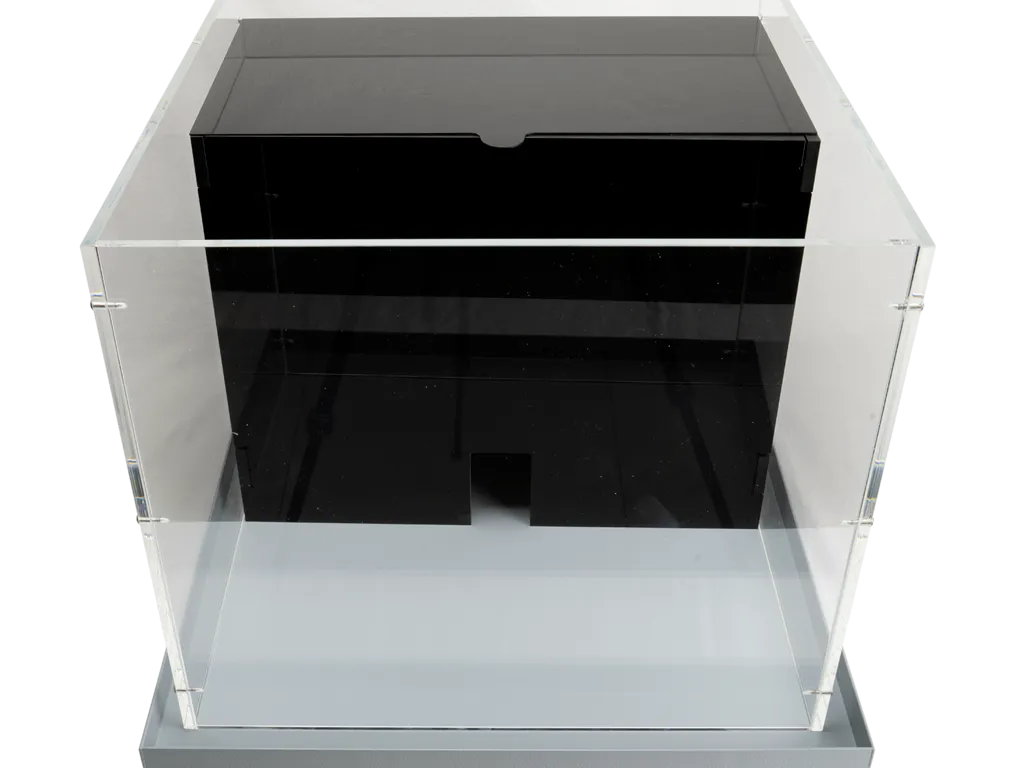

Light-dark box
The light-dark box is used to test the unconditioned anxiety response, based on the novel environment and the light/open space.
Fear conditioning
Fear conditioning and other learning tasks in rodents are typical in a wide range of neuropharmacological studies, amongst others.
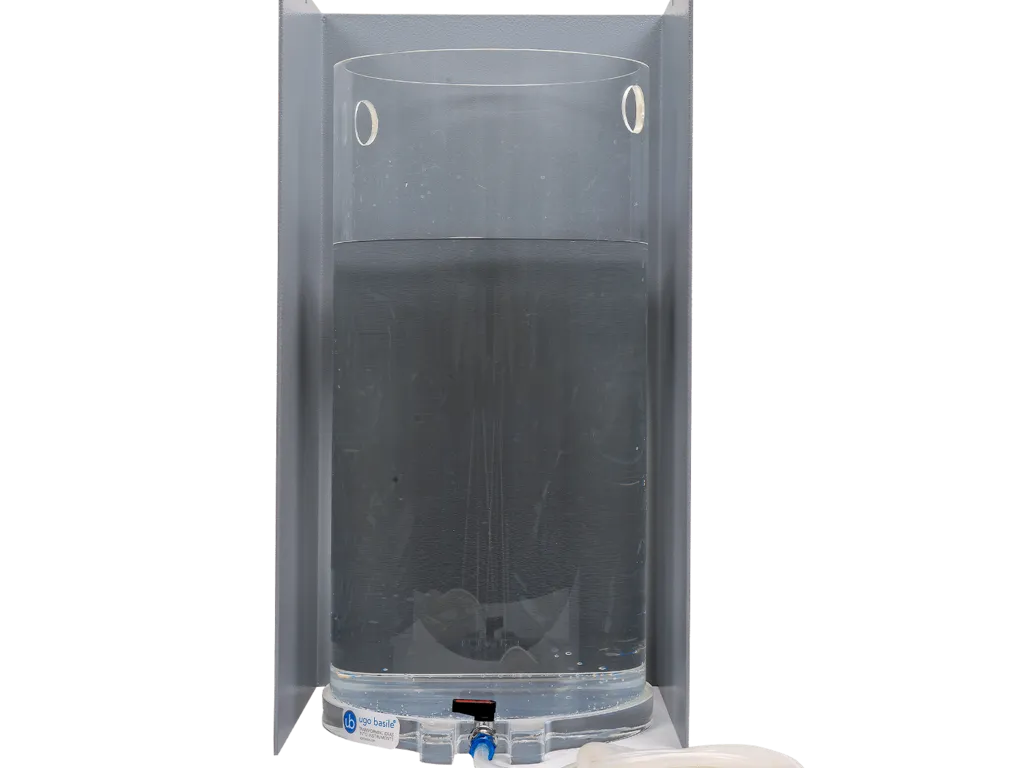

Forced swim test
The (Porsolt) forced swim test, also known as the behavioral despair test, is used to test for depression-like behavior in both mice and rats.
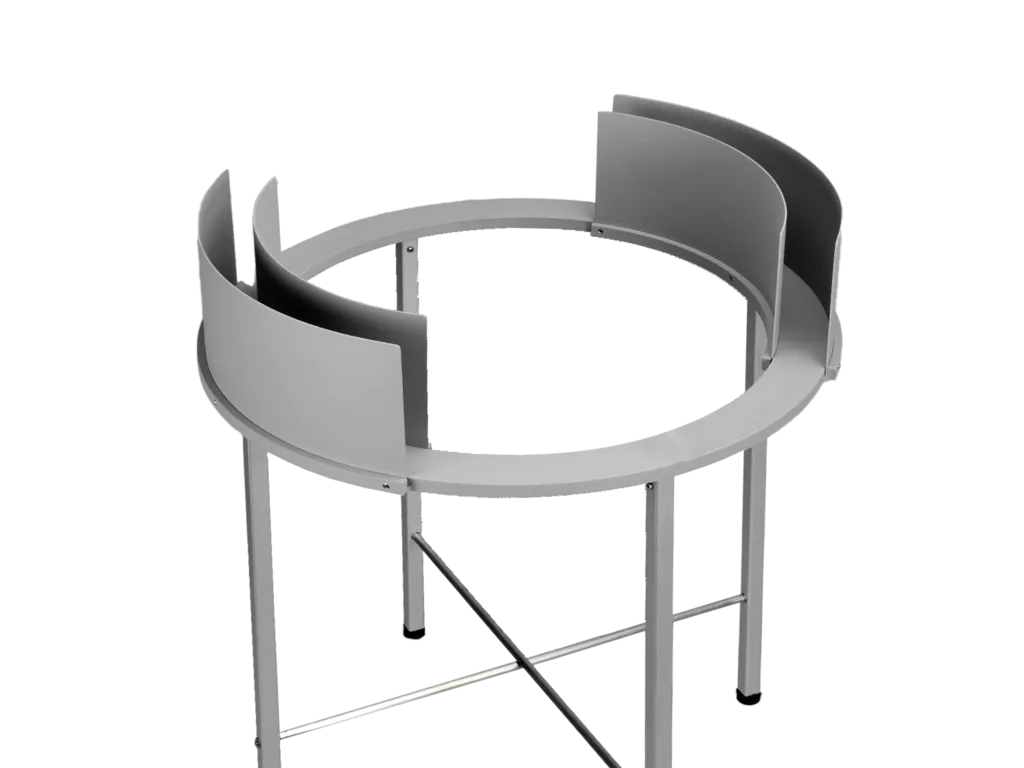

Zero maze
The elevated zero maze is very similar to the elevated plus maze, but lacks a center square. Gives an indication of anxiety versus exploration.
Anxiety and stress in zebrafish
Zebrafish display stress and anxiety-like behaviors by displaying
bottom dwelling behavior. In laboratory settings, important measurements are the time spent in the
bottom of a novel tank, as well as latency to explore the upper half. These are useful parameters in
the study of anxiolytic and anxiogenic properties of certain compounds.
Side-view tracking
is a practical approach to measure these parameters. This is an easy task for EthoVision XT .
Methods for studying anxiety and stress in zebrafish

Novel tank diving test
Bottom dwelling behavior and latency to exploring the upper half of the tank are important measures that indicate stress and anxiety.
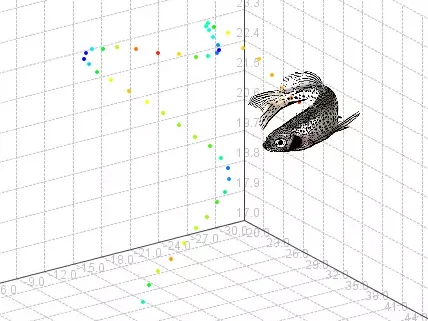
Track3D
Tracking in three dimensions is a true assessment of path shape, erratic movement, and velocity that cannot be fully measured from a side or top view.
Using EthoVision XT to study fear, anxiety, and stress
Fear conditioning
Fear- a highly conserved behavior in rodents. EthoVision XT easily automates this test and accurately measures freezing behavior.
Novel tank diving test
EthoVision XT is well-established in measuring bottom dwelling behavior and latency to explore in the novel tank diving test.
Elevated plus maze
The elevated plus is the most used test to study anxiety and exploration in rats and mice. It is also a test that can be easily automated using EthoVision XT.
Don't know where to start?
We're happy to help
Book a meeting for an online or onsite session.
Together, we can discuss your research requirements and come up with the best solution!