What is Galvanic Skin Response?
Understanding human emotions and physiological responses is a key focus in behavioral science. One insightful tool in this field is galvanic skin response (GSR). But what is galvanic skin response? A beginner’s guide to understanding GSR in research.
Posted by
Published on
Fri 07 Feb. 2025
Topics
| Behavioral Research | Emotion Recognition | Measure Emotions | Mental Workload | Methods And Techniques | Physiology |

Understanding human emotions and physiological responses is relevant in many areas of behavioral science. One of the most effective ways to measure these responses is through galvanic skin response (GSR), also known as electrodermal activity (EDA). But what exactly is GSR, and why is it so important in behavioral research?
What is galvanic skin response?
The galvanic skin response refers to the measurement of the skin’s electrical conductance, which changes with sweat gland activity. This activity is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. This means it reacts automatically when you feel emotions like stress, fear, or excitement.
When you experience emotional arousal, your sweat glands become more active, leading to increased skin conductance. Measuring these changes allows researchers to gain insights into the body’s unconscious responses, revealing key information about emotional and psychological states.
How is galvanic skin response measured?
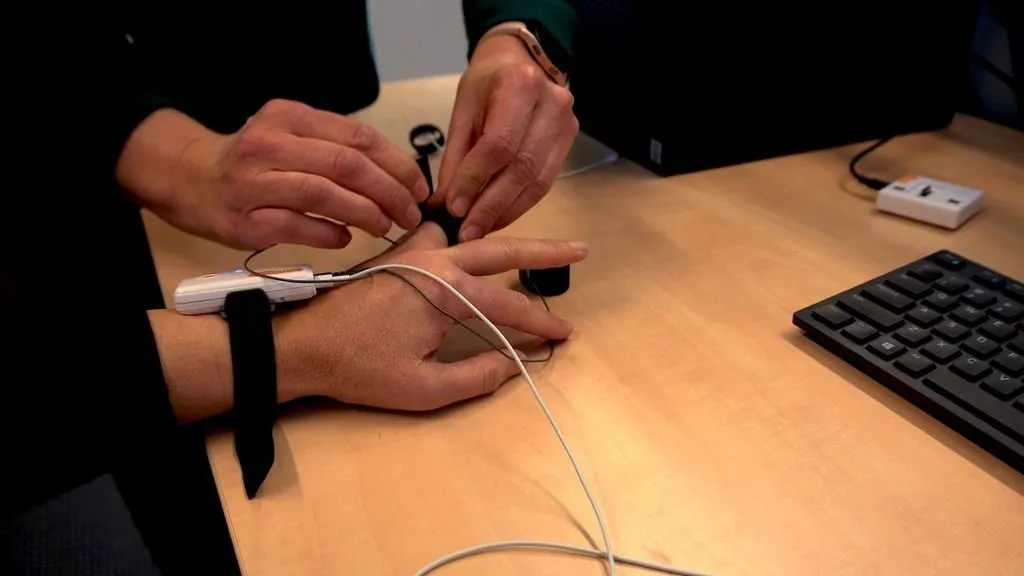
Galvanic skin response is measured using small electrodes placed on the skin, typically on the fingers or palms, where sweat gland activity is most noticeable. These electrodes detect the skin’s electrical conductance between two points, which changes with sweat production.
The process of measuring electrodermal activity includes the following steps:
- Electrode placement: Electrodes are attached to the participant’s skin, usually on the fingertips or palm.
- Baseline recording: Before introducing stimuli, a baseline is recorded to understand the participant’s normal or current state.
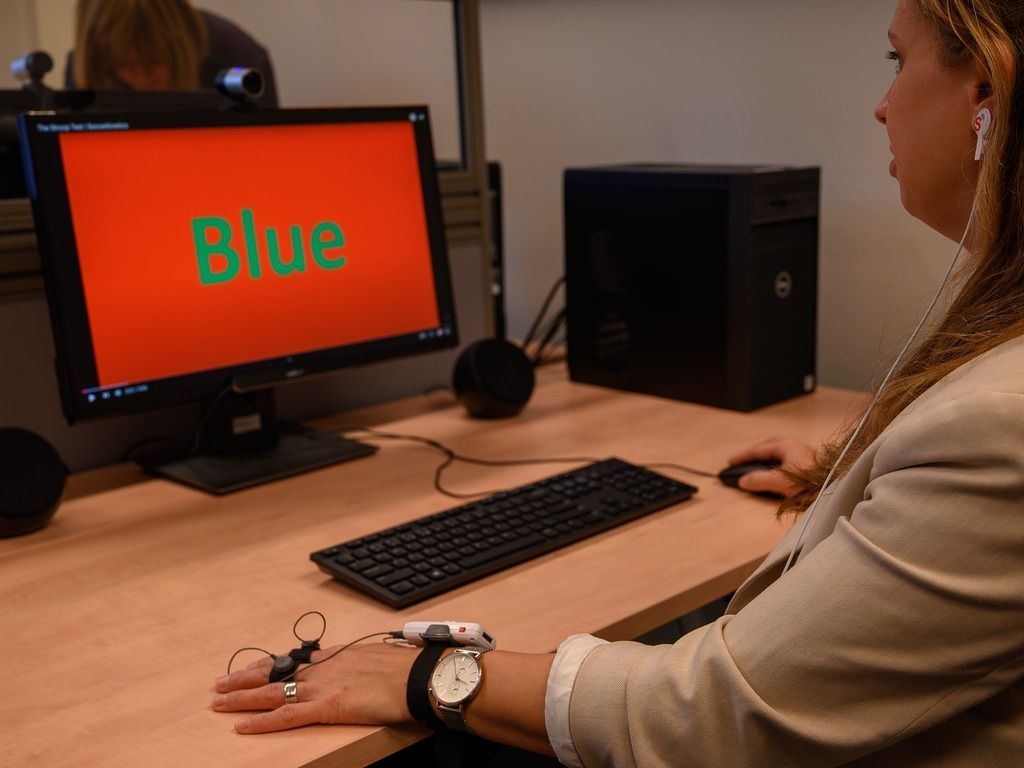
- Stimulus introduction: Participants are exposed to stimuli, such as images, sounds, or tasks specifically designed to evoke emotional reactions.
- Data collection: The system tracks changes in skin conductance as the participant responds, producing real-time data displayed on a graph.
This simple yet effective method provides researchers with a continuous measure of physiological arousal during behavioral experiments.
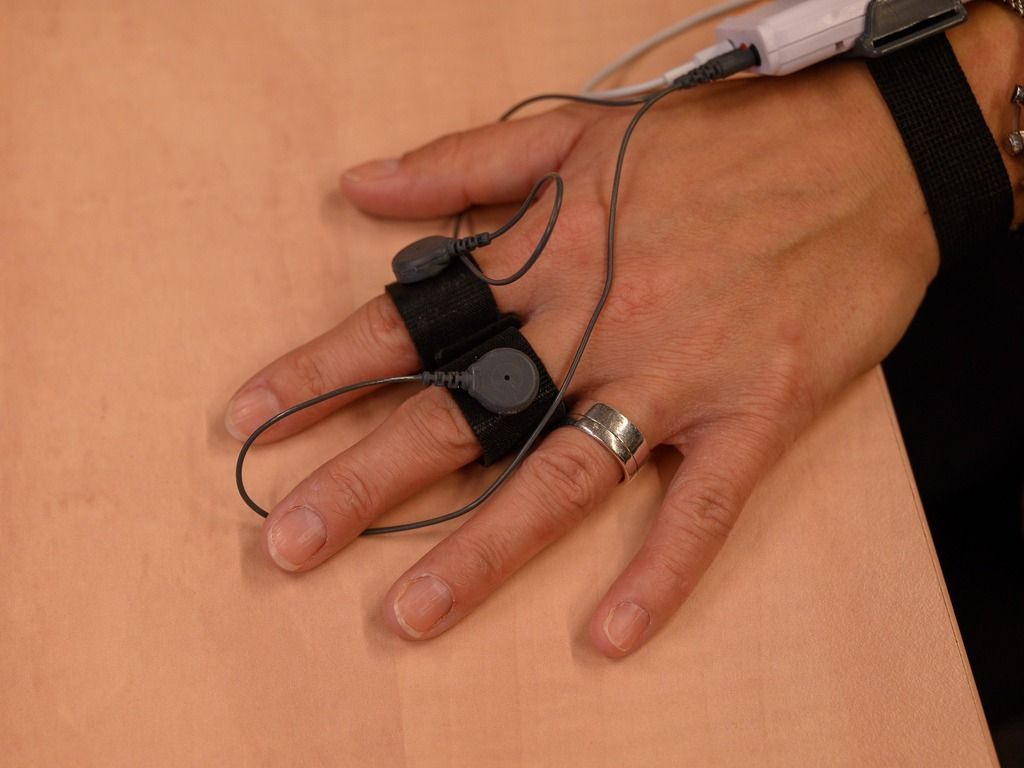
How is galvanic skin response used in behavioral research
Galvanic skin response has become a valuable tool in behavioral science because it provides objective, real-time data on emotional arousal. Unlike self-reported data, which can be biased or inaccurate, GSR directly measures unconscious physical responses. This makes it ideal for studies where understanding true emotional reactions is critical.
Some key applications where galvanic skin response is a valuable measurement tool:
- Emotion research: Galvanic skin response is widely used to study how different stimuli affect emotional states. For instance, researchers can analyze how a participant's skin conductance changes in response to positive or negative images, providing insights into emotional processing.
- Stress and anxiety studies: In research on stress and anxiety, electrodermal activity can reveal how participants physiologically react to stressors, helping researchers develop better interventions and treatments.
- Human-Computer Interaction (HCI): GSR is employed to assess user experience by measuring emotional responses to different interface designs or software usability, aiding in the development of more user-friendly technologies.
- Marketing research: Neuromarketers use electrodermal activity to gauge consumer reactions to advertisements, products, or brand experiences, offering deeper insights into consumer behavior beyond what traditional surveys can reveal.
By measuring the electrical conductance of the skin, galvanic skin response (GSR) provides an objective, real-time view of how people respond to various stimuli. This makes it a critical tool in psychology, neuroscience, marketing, and many more fields.
What makes GSR a valuable tool for studying emotions?
GSR offers unique insights into the physiological underpinnings of human emotions and reactions, particularly the intensity and timing of emotional responses.
For example, in marketing, GSR can reveal how consumers react to advertisements, helping companies tailor their strategies. In psychology research it can be used to study anxiety levels in patients during therapy sessions.
What sets GSR apart is its ability to detect unconscious physiological responses tied to emotional arousal. Unlike self-reports, which rely on conscious sharing, GSR measures the body's automatic reactions. This provides researchers with clear, unbiased data and a more accurate view of how emotions influence behavior.

Limitations and considerations of GSR
GSR offers unique insights into the physiological underpinnings of human emotions and reactions, particularly the intensity and timing of emotional responses.
For example, in marketing, GSR can reveal how consumers react to advertisements, helping companies tailor their strategies. In psychology research it can be used to study anxiety levels in patients during therapy sessions.
What sets GSR apart is its ability to detect unconscious physiological responses tied to emotional arousal. Unlike self-reports, which rely on conscious sharing, GSR measures the body's automatic reactions. This provides researchers with clear, unbiased data and a more accurate view of how emotions influence behavior.

While GSR is a powerful tool, it's important to remember that it measures arousal rather than specific emotions. For example, increased skin conductance might indicate excitement or fear; it’s the context that helps determine the meaning. To get a more complete picture, GSR is often combined with other methods, like facial expression analysis and heart rate monitoring
Additionally, environmental factors like room temperature and humidity, as well as the participant's level of hydration, can influence GSR readings. Researchers must carefully control these variables to ensure accurate and reliable data. Analysis tools like FaceReader or NoldusHub can help with objective measurement and assessment of this kind of data.
Using GSR for better insights in human behavior
The galvanic skin response is invaluable for human behavior studies. By measuring changes in skin conductance, GSR provides unique, objective insights into emotional arousal and physiological responses. Whether you’re studying emotions, stress, or user experiences, including GSR in your research can provide deeper discoveries in behavioral science.
NOLDUSHUB: Your data in a heartbeat
Discover how NoldusHub benefits your research, and why it is the best multimodal platform for you to use:
- Clean and easy to use interface
- Synchronization from the start
- Powerful data visualizations
Related Posts

Predicting Advertising Effectiveness: Facial Coding of 120.000 Video Frames

World Cup success and emotions
